Figure 2https://media.springernature.com/full/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1186%2F2044-5040-4-11/MediaObjects/13395_2014_Article_102_Fig2_HTML.jpg?as=webp
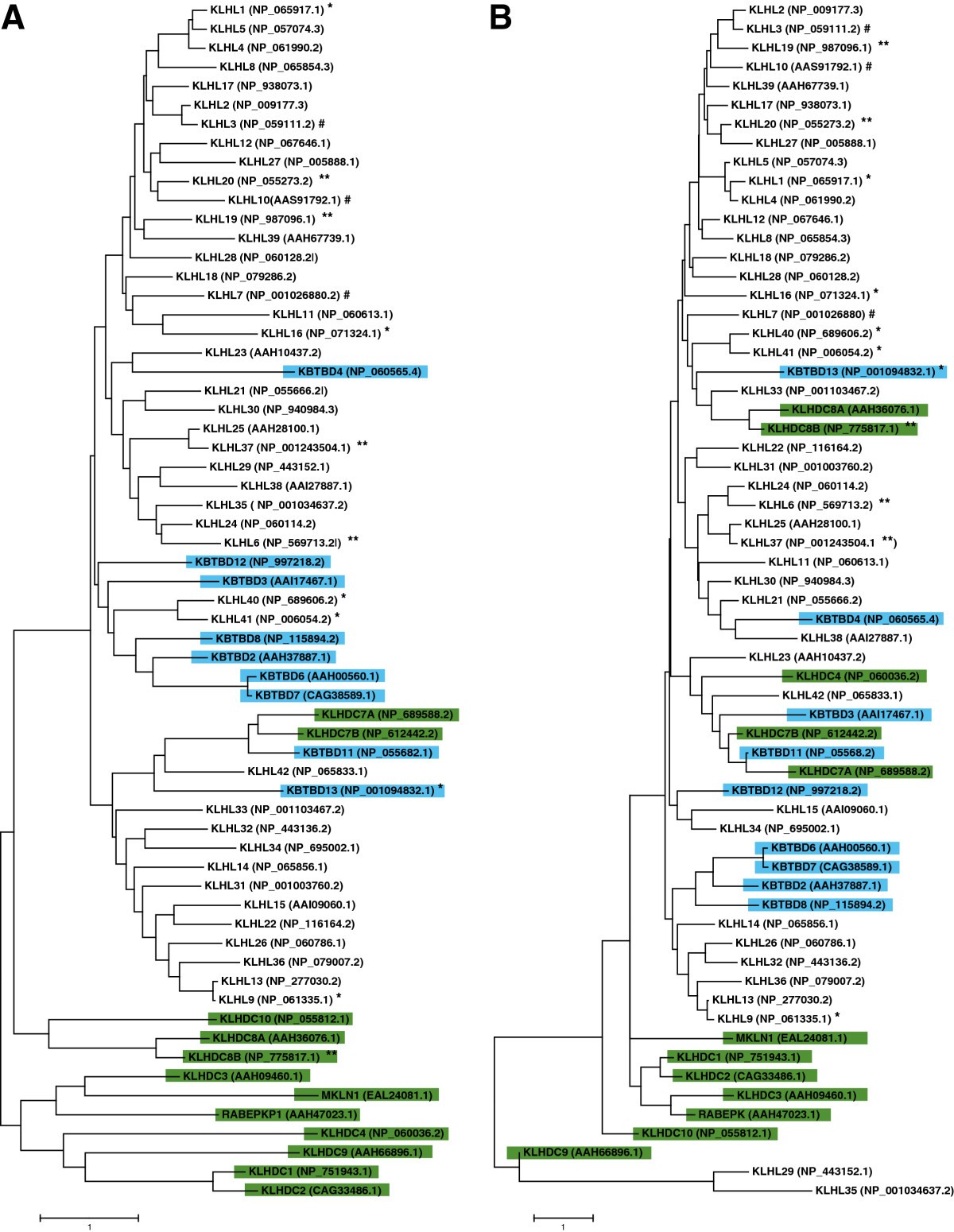
The Kelch Superfamily. (A) The Kelch family consists of 63 proteins that are subclassified in to KLHL, KBTBD and KLHDC subfamilies. (B) Structure of Kelch domain of rat KLHL41 (PDB code 2WOZ) comprising six repeats that form the complete Kelch domain. The structure was generated using PyMOL (http://www.pymol.org)
. (C) Prototype members of different subfamilies showing different domain organization.
KLHL proteins have an N-terminal BTB/POZ, a BACK and C-terminal Kelch repeats.
KBTBD proteins contain an N-terminal BTB domain and Kelch repeats. The BACK domain is normally absent in KBTBD proteins.
KLHDC proteins lack both BTB/POZ and BACK domains and contain either Kelch repeats alone or with other domains such as transmembrane (for example, KLHDC7A), Glycine rich (for example, KLHDC10), or Lish and CTLH domains (for example, MKLN1).

Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar