Englanninkielinen wikipediatieto on hyvåä, joten otan sen tässä esiin ja suomennan kappale kappaleelta.
Efriini, engl. Ephrin
|
EPH-reseptorit taas ovat tunnettujen reseptoriproteiini-tyrosiinikinaasien (RTK) alaperheistä laajin.
- Ephrins (also known as ephrin ligands or Eph family receptor interacting proteins) are a family of proteins that serve as the ligands of the eph receptor. Eph receptors in turn compose the largest known subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases (RTKs).
EPH/efriini-signaloinnin intrasellulaaristen ( solunsisäisten) teitten aktivoituminen voi tapahtua ainoastaan suoran solu-solu-kontaktin välittämänä. EPH/efriini-signalointi säätelee monenlaisia biologisia prosesseja alkion kehityksen aikana ja niihin kuuluu aksonien kasvukartioiden( kasvukeilojen) ohjaus, kudosten rajojen muodostaminen, solumigraatio ja segmentoituminen ( jaoksien muodostuminen). Lisäksi EPH/efriini-signalointi on äskettäin tunnistettu ratkaisevaksi osatekijäksi myös useiden aikuiskehossa tapahtuvien prosessien ylläpidossa. Näihin kuuluu muistin latautuminen, pitkäaikaispotentioituminen (LTP), angiogeneesi ja kantasolun erilaistuminen
- Since ephrin ligands (ephrins) and Eph receptors (Ephs) are both membrane-bound proteins, binding and activation of Eph/ephrin intracellular signaling pathways can only occur via direct cell-cell interaction. Eph/ephrin signaling regulates a variety of biological processes during embryonic development including the guidance of axon growth cones,[1] formation of tissue boundaries,[2] cell migration, and segmentation.[3] Additionally, Eph/ephrin signaling has recently been identified to play a critical role in the maintenance of several processes during adulthood including long-term potentiation,[4] angiogenesis,[5] and stem cell differentiation.[6]
Luokittelu, engl. Classification
Efriiniligandit jaetaan kahteen alaluokkaan rakenteen ja kalvoonkytkeytymistavan perusteella. Ne ovat A-tyypin efriinit ja B-tyypin efriinit.A-tyypin efriineillä on GPI-kalvoankkuri (glykosyylifosfatidyyli-inositoli-liitos) ja niiltä puuttuu sytoplasminen domeeni.
B-tyypin efriinit liittyvät kalvoon lyhyellä TM- domeenilla ( transmembraaninen, kalvon läpäisevä jakso). Siinä on lyhyt sytoplasminen PDZ :iä sitova motiivi.
A- ja B-tyypin efriinejä koodaavat geenit ovat vastaavasti EFNA ja EFNB .
EPH-reseptorit puolestaan luokitellaan joko EPHA tai EPHB - reseptoreiksi sen perusteella onko niillä affiniteettia A vai B-tyypin efriiniligandeihin.
- Ephrin ligands are divided into two subclasses of ephrin-A and ephrin-B based on their structure and linkage to the cell membrane. Ephrin-As are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) linkage and lack a cytoplasmic domain, while ephrin-Bs are attached to the membrane by a single transmembrane domain that contains a short cytoplasmic PDZ-binding motif. The genes that encode the ephrin-A and ephrin-B proteins are designated as EFNA and EFNB respectively. Eph receptors in turn are classified as either EphAs or EphBs based on their binding affinity for either the ephrin-A or ephrin-B ligands.[7]
- Of the eight ephrins that have been identified in humans there are five known ephrin-A ligands (ephrin-A1-5) that interact with nine EphAs (EphA1-8 and EphA10) and three ephrin-B ligands (ephrin-B1-3) that interact with five EphBs (EphB1-4 and EphB6).[4][8] Ephs of a particular subclass demonstrate an ability to bind with high affinity to all ephrins of the corresponding subclass, but in general have little to no cross-binding to ephrins of the opposing subclass.[9] However, there are a few exceptions this intrasubclass binding specificity as it has recently been shown that ephrin-B3 is able bind to and activate EPH receptor A4 and ephrin-A5 can bind to and activate Eph receptor B2.[10]
Sitävastoin EPHB-reseptorit sitovat matalammalla affiniteetilla omaakin ligandiaan kuin EPHA/Efriini-A- sitoutumisissa, koska ne hyödyntävät 2indusoitua sovitusmekanismia" (induced fit-mechanism), joka vaatii suurempaa struktuurin muutosta EPHB- reseptoreilta, kun ne sitoutuvat B-tyypin efriiniligandeihinsa.
- EphAs/ephrin-As typically bind with high affinity, which can partially be attributed to the fact that ephrinAs interact with EphAs by a "lock-and-key" mechanism that requires little conformational change of the EphAs upon ligand binding. In contrast EphBs typically bind with low affinity than EphAs/ephring-As since they utilize an "induced fit" mechanism that requires a greater conformational change of EphBs to bind ephrin-Bs.[1
Toiminta, Engl. Function
Aksonin ohjaus, Engl. Axon guidance
Keskushermostojärjestelmän kehityksen aikana EPH/efriini-signaloinnilla on ratkaiseva osa useiden neuronityyppien aksoneiden solu-solu-välitteisessä migraatiossa lopulliseen kohteeseensa. EPH/efriini-signalointi kontrolloi hermosolun aksonin (= impulssin viejähaarake) ohjautumista kyvyllänsä estää aksonin kasvukartion elossapysyminen karkoittamalla migroivaa aksonia poispäin EPH/efriinin aktivaatiokohdasta. Migroivan aksonin kasvukartiot ( kasvukeilat) eivät vastaa suoraan EPH- reseptoreiden tai efriinien absoluuttisiin pitoisuuksiin kontaktisoluissaan, vaan pikemminkin ne vastaavat EPH-reseptorien ja efriinin ilmentymän suhteelliseen pitoisuuteen, mikä sallii migroituvien aksonien ( joissa on joko EFP-reseptoreita tai efriiniligandeja) johtua solujen ilmentämien EPH- tai efriini-gradienttien mukaisesti kohti sellaista päämäärää ( kujanjuoksun tapaan), jossa aksonin kasvukeilan elossapysyminen ei enää tulee täydellisesti estetyksi.- During the development of the central nervous system Eph/ephrin signaling plays a critical role in the cell-cell mediated migration of several types of neuronal axons to their target destinations. Eph/ephrin signaling controls the guidance of neuronal axons through their ability to inhibit the survival of axonal growth cones, which repels the migrating axon away from the site of Eph/ephrin activation.[12] The growth cones of migrating axons do not simply respond to absolute levels of Ephs or ephrins in cells that they contact, but rather respond to relative levels of Eph and ephrin expression,[13] which allows migrating axons that express either Ephs or ephrins to be directed along gradients of Eph or ephrin expressing cells towards a destination where axonal growth cone survival is no longer completely inhibited.[12]
- Although Eph-ephrin activation is usually associated with decreased growth cone survival and the repellence of migrating axons, it has recently been demonstrated that growth cone survival does not depend just on Eph-ephrin activation, but rather on the differential effects of "forward" signaling by the Eph receptor or "reverse" signaling by the ephrin ligand on growth cone survival.[12][14]
Verkkokalvo (Retina), retinotooppinen kartoittuminen
Retinotopic mapping
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S14_7JSeWkM
Järjestäytyneen retinotooppisen kartan muodostuminen Colliculus-superior-tumakkeeseen vaatii retinan gangliosolujen aksonien asianmukaisen migroitumisen verkkokalvosta Colliculus-superior-tumakkeen spesifisille alueille ( alemmilla selkärankaisilla : optinen tectum-alue; katso videopätkä) Tämä aksonien migroituminen välittyy EPH- reseptorien ja niiden ligandien efriinien ilmentymisten gradienteilla Colliculus superiorissa ja verkkokalvosta migroitumaan lähtevissä gangliosoluissa. Aksonaalisen asvukärjen alentunut elossapysyminen, josta yllä mainittiin, sallii korkean posteriorisen/ matalan anteriorisen Efriini-A-gradientin Colliculus superiorissa johtaa retinan gangliosolujen aksoneita retinan temporaalisilta (ohimon puolisilta) alueilta ( jossa on korkea EPHAreseptoripitoisuus) kohti päämääriä, jotka ovat etuosissa ( anteriorisesti) Colliculus superioria; ja retinan nenän puoleisilta ( matala EPHA-reseptori-ilmenemä) kohti päämääriä, jotka ovat takaosissa( posteriorisesti) Colliculus superioria.Samalla tavalla johtaa Efriini-B1-ilmenemän gradientti aksonimigraatiota retinan gangliosoluista , jotka ilmentävät EPHB gradienttia. Colliculus superior ilmentää efriiniB1-ligandin gradienttia Tämä gradienttiilmenemä johtaa migraatiota Retinan taka- ja etuosista Colliculus superiorin ulkosivun puolisiin (lateraalisiin) ja sisäsivun puoliin ( mediaalisiin) osiin .
(Colliculus superior sijaitsee isoaivojen peitossa keskiaivojen selän nelikukkulassa Quadrigemina, jossa on 4 pyöreää paksunnosta ja kaksi ylempää niistä ovat nimeltään colliculus superior, niitä on siis kaksi kappaletta, oikean ja vasemman puolinen, niitten kautta menee näköradat. Niillä on toinenkin nimi: Corpus geniculatum laterale, koska näkö rata tekee polvimaisesti näissä kappaleissa mutkan. Genus = polvi, corpus = kappale)
- The formation of an organized retinotopic map in the superior colliculus (SC) (referred to as the optic tectum in lower vertebrates) requires the proper migration of the axons of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) from the retina to specific regions in the SC that is mediated by gradients of Eph and ephrin expression in both the SC and in migrating RGCs leaving the retina.[15] The decreased survival of axonal growth cones discussed above allows for a gradient of high posterior to low anterior ephrin-A ligand expression in the SC to direct migrating RGCs axons from the temporal region of the retina that express a high level of EphA receptors toward targets in the anterior SC and RGCs from the nasal retina that have low EphA expression toward their final destination in the posterior SC.[16][17][18] Similarly, a gradient of ephrin-B1 expression along the medial-ventral axis of the SC directs the migration of dorsal and ventral EphB-expressing RGCs to the lateral and medial SC respectively.[19]
Angiogeneesi, Angiogenesis
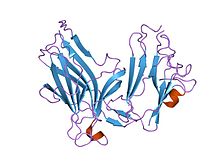
KUVA. EPHB4 reseptoriproteiini tunentaan kehityksen aikaisena proteiinina sekä tuumorin angiogeneesissä esiintyvänä.
The EphB4 receptor protein, known to assist in developmental and tumor angiogenesis.
Efriinit edistävät fysiologista ja patologista angiogeneesiä 8 esim syövän angiogeneesi, neovaskularisaatio aivon arteriovenöösissä epämuodostumassa) Erityissti efriini-B2 ja EPHB4-reseptori määräävät valtimon ja vastaavsti laskimon kohtalosta endoteelisoluissa säätelemällä angiogeneesiä lieventäen VEGF- signaalitien ilmentymistä. Efriini-B2 vaikuttaa VEGF- reseptoreihin ( esim VEGFR3) eteenpäin ja käänteisesti suuntautuvilla signalointiteille. Efriinik-B2 signaalitie ulottuu lymfangiogeneesiuin asti johtaen VEGFR3 reseptorfeiden internalisoitumiseen viljeltyihin lymfaattisiin endoteelisoluihin.
On selvitetty efriinien osuus kehityksenaikaisessa angiogeneesissä, mutta tuumoriangiogeneesi on edelleen pysynyt epäselvänä. EfriiniA2- puutteisista hiiristä tehtyjen havaintojen mukaan efriini-A2 saattaa toimia antamalla signaaleja eteenpäin tuumorin angiogeneesissä, muta tämä efriini ei osallistu kehityksenaikaisiin verisuoniston epämuodostumiin. Lisäksi Efriini-B2 ja reseptori EPHB4 saattavat osallistua tuumorin angiogeneesiin kehityksen aikaisen asemansa lisäksi, vaikka tarkka mekanismi pysyykin tuntemattomana. Efriini-B2/EPHB4 ja Efriini-B3/EPHB1- reseptoriparit osallistuvat enempikin verisuonten muodostumiseen angiogeneesin ohella, kun taas Efriini-A1/EPHA2 näyttää osallistuvan ainoastaan angiogeneesiin.
- Ephrins promote angiogenesis in physiological and pathological conditions (e.g. cancer angiogenesis, neovascularisation in cerebral arteriovenous malformation).[20][21] In particular, Ephrin-B2 and EphB4 determine the arterial and venous fate of endothelial cells, respectively, though regulation of angiogenesis by mitigating expression in the VEGF signalling pathway.[20][22] Ephrin-B2 affects VEGF-receptors (e.g.VEGFR3) through forward and reverse signalling pathways.[22] The Ephrin-B2 path extends to lymphangiogenesis, leading to internalization of VEGFR3 in cultured lymphatic endothelial cells.[22] Though the role of ephrins in developmental angiogenesis is elucidated, tumor angiogenesis remains nebulous. Based on observations in Ephrin-A2 deficient mice, Ephrin-A2 may function in forward signalling in tumor angiogenesis; however, this ephrin does not contribute to vascular deformities during development.[23] Moreover, Ephrin-B2 and EphB4 may also contribute to tumor angiogenesis in addition to their positions in development, though the exact mechanism remains unclear.[23] The Ephrin B2/EphB4 and Ephrin B3/EphB1 receptor pairs contribute more to vasculogenesis in addition to angiogenesis whilst Ephrin A1/EphA2 appear to exclusively contribute to angiogenesis.[24]
- Several types of Ephrins and Eph receptors have been found to be upregulated in human cancers including breast, colon and liver cancers.[24] Surprisingly, the downregulation of other types of Ephrins and their receptors may also contribute to tumorigenesis; namely, EphA1 in colorectal cancers and EphB6 in melanoma.[24] Displaying similar utility, different ephrins incorporate similar mechanistic pathways to supplement growth of different structures.
Migraatiotekijä suoliston epitelisolun migroitumisessa
Engl. Migration factor in intestinal epithelial cell migration
Migraatiota aiheuttaa bidirektionaalinen signalointimekanismi, jossa efriiniligandi/EPHB reseptori-vuorovaikutus säätelee aktiinisytoskeletonin dynamiikkaa aiheuttaen "repulsiota". Solu jää paikoilleen, kun reseptori-ligandi-interaktio loppuu. Gobletin solut, jotka erittävät limaa ( mucus) ja absorboivat solut liikkuvat suolen luumenia (onteloa) päin, kun taas kypsät Panethin solut liikkuvat vastapäiseen suuntaan, kryptan pohjiin, jossa niitten paikka on. Suolesta on havaittu kaikki muita luokan A ja B proteiineja paitsi EPH5 -reseptoriin sitoutuvaa ligandia. Kuitenkin efriiniproteiineja efriini -A4, -A8, -B2 ja -B4 esiintyy korkeimmat pitoisuudet sikiöasteella ja pitoisuus alenee iän mukana.- The ephrin protein family of class A and class B guides ligands with the EphB family cell-surface receptors to provide a steady, ordered, and specific migration of the intestinal epithelial cells from the crypt[clarification needed] to villus. The Wnt protein triggers expression of the EphB receptors deep within the crypt, leading to decreased Eph expression and increased ephrin ligand expression, the more superficial a progenitor cell's placement.[25] Migration is caused by a bi-directional signaling mechanism in which the engagement of the ephrin ligand with the EphB receptor regulates the actin cytoskeleton dynamics to cause a "repulsion". Cell remain in place once the interaction ceases to a stop. While the mucus secreting Goblet cells and the absorptive cells move towards the lumen, mature Paneth cells move in the opposite direction, to the bottom of the crypt, where they reside.[26] With the exception of the ephrin ligand binding to EphA5, all other proteins from class A and B have been found in the intestine. However, ephrin proteins A4, A8, B2, and B4 have highest levels in fetal stage, and decline with age.
(APC, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenomatous_polyposis_coli )
- Experiment done with Eph receptor knockout mice revealed disorder in the distribution of different cell types.[26] Absorptive cells of various differentiation were mixed with the stem cells within the villi. Without the receptor, the Ephrin ligand was proved to be insufficient for the correct cell placement.[27] Recent studies with knockout mice have also shown evidence of the ephrin-eph interaction indirect role in the suppression of colorectal cancer. The development of adenomatous polyps created by uncontrolled outgrowth of epithelial cells is controlled by ephrin-eph interaction. Mice with APC mutation, without ephrin-B protein lack the means to prevent the spread of ephB positive tumor cells throughout the crypt-villi junction.[28]
Käänteissuuntainen signalointi, Reverse signaling
Efriini-ligandien ainutlaatuinen ominaisuus on kyky aloittaa käänteissuuntainen signaali, joka on erillinen ja erotettavissa EPH-reseptoria ilmentävissä soluissa aktivoituneesta intrasellulaarisesta signaalista. Vaikka ei aivan täydellisesti ymmärretäkään sitä mekanismia, jolla käänteinen signalointi tapahtuu, niin molemmat efriinityypit A ja B ovat näyttäneet välittävän sellaisia soluvasteita, jotka ovaat erillään niistä vasteista, jotka assosioituvat niiden reseptorien aktivaatioon.Erityisesti efriini-5B on näyttänyt stimuloivan spinaalisen motorisen neuronin kasvukärjen leviämistä ja efriini-B1 on näyttänyt edistävän dendriittiharakkeen kypsymistä.
One unique property of the ephrin ligands is that many have the capacity to initiate a "reverse" signal that is separate and distinct from the intracellular signal activated in Eph receptor-expressing cells. Although the mechanisms by which "reverse" signaling occurs are not completely understood, both ephrin-As and ephrin-Bs have been shown to mediate cellular responses that are distinct from those associated with activation of their corresponding receptors. Specifically, ephrin-A5 was shown to stimulate growth cone spreading in spinal motor neurons[12] and ephrin-B1 was shown to promote dendritic spine maturation.[29]
Kommentti: Wikipediateksti englanniksi oli asetettu viime vuoden elokuussa ja artikkeliin liittyy useita referaatteja, jotka saa alussa olevasta linkistä. Muistiin 13.3. 2019