settings
Cells
2019,
8(3),
214;
https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030214
Review
Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and the Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
Received: 5 February 2019 / Accepted: 26 February 2019 / Published: 3 March 2019
Abstract
Oxygen deprivation or hypoxia characterizes a number
of serious pathological conditions and elicits a number of adaptive
changes that are mainly mediated at the transcriptional level by the
family of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs).
The HIF target gene
repertoire includes genes responsible for the regulation of metabolism,
oxygen delivery and cell survival. Although the involvement of HIFs in
the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism and the switch to anaerobic
glycolysis under hypoxia is well established, their role in the control
of lipid anabolism and catabolism remains still relatively obscure.
Recent evidence indicates that many aspects of lipid metabolism are
modified during hypoxia or in tumor cells in a HIF-dependent manner,
contributing significantly to the pathogenesis and/or progression of
cancer and metabolic disorders.
However, direct transcriptional
regulation by HIFs has been only demonstrated in relatively few cases,
leaving open the exact and isoform-specific mechanisms that underlie
HIF-dependency. This review summarizes the evidence for both direct and
indirect roles of HIFs in the regulation of genes involved in lipid
metabolism as well as the involvement of HIFs in various diseases as
demonstrated by studies with transgenic animal models.
Keywords:
hypoxia; HIF; lipids; metabolism; cancer
--
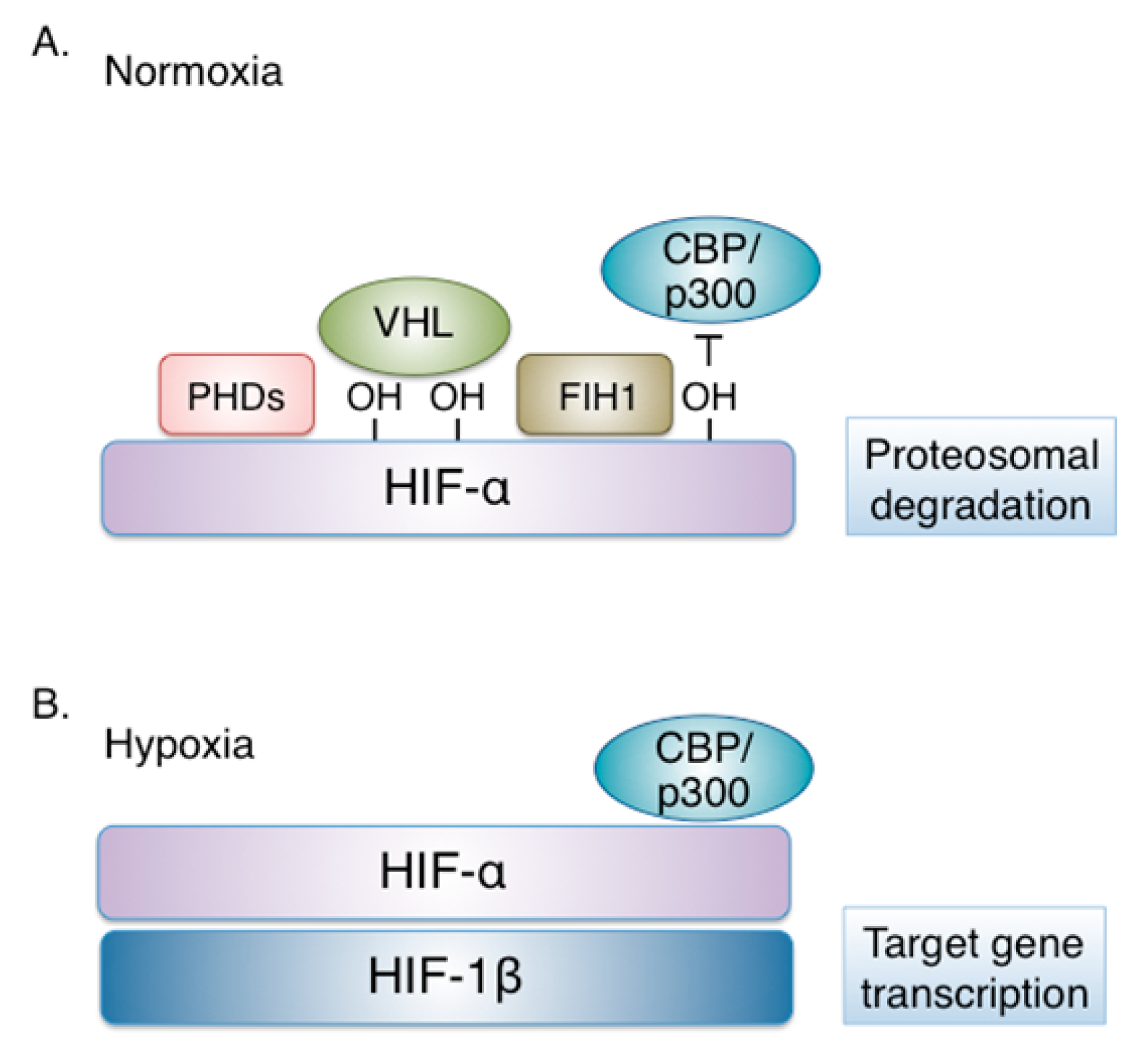
HIFs are heterodimeric transcription factors that consist of an oxygen regulated alpha subunit and a constitutively expressed beta subunit, also known as ARNT (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator), both members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins of the PER-ARNT-SIM (PAS) DNA binding protein family.
The active heterodimer binds to hypoxia-response elements (HREs) on the promoter or enhancer regions of target genes, causing their transcriptional activation [2].
Three HIF-α isoforms have been identified to date.
HIF-1α is expressed ubiquitously in cells and tissues, while,
HIF-2α (termed also EPAS1) is tissue specific [3,4].
The third and least studied HIF-α isoform, HIF-3α, exists in multiple splice variants most of which act as dominant-negative regulators of HIF activity [5,6].
Post-translationally, in addition to hydroxylation, HIF-1α is subject to SUMOylation [17,18,19,20], acetylation [21,22], deacetylation [23] and S-nitrosylation [24], although the impact of these modifications on HIF-1α stability and/or activity has not yet been adequately clarified. In contrast, direct phosphorylation by several kinases is important for HIF-1α regulation and is extensively studied (reviewed in [25]) (Figure 2).
HIFs are heterodimeric transcription factors that consist of an oxygen regulated alpha subunit and a constitutively expressed beta subunit, also known as ARNT (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator), both members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins of the PER-ARNT-SIM (PAS) DNA binding protein family.
The active heterodimer binds to hypoxia-response elements (HREs) on the promoter or enhancer regions of target genes, causing their transcriptional activation [2].
Three HIF-α isoforms have been identified to date.
HIF-1α is expressed ubiquitously in cells and tissues, while,
HIF-2α (termed also EPAS1) is tissue specific [3,4].
The third and least studied HIF-α isoform, HIF-3α, exists in multiple splice variants most of which act as dominant-negative regulators of HIF activity [5,6].
Post-translationally, in addition to hydroxylation, HIF-1α is subject to SUMOylation [17,18,19,20], acetylation [21,22], deacetylation [23] and S-nitrosylation [24], although the impact of these modifications on HIF-1α stability and/or activity has not yet been adequately clarified. In contrast, direct phosphorylation by several kinases is important for HIF-1α regulation and is extensively studied (reviewed in [25]) (Figure 2).

24.10.2019. TIETOA HIF2alfasta:
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Sep 23;413(2):201-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.08.058. Epub 2011 Aug 24.
Kelch-like
20 up-regulates the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α through
hypoxia- and von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein-independent
regulatory mechanisms.Higashimura Y1, Terai T, Yamaji R, Mitani T, Ogawa M, Harada N, Inui H, Nakano Y. Abstract Despite
their structural similarity, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and
HIF-2α have distinct functional properties and exhibit distinct
spatiotemporal expression patterns, suggesting that the expressions of
the two proteins are regulated by different mechanisms. To clarify the
HIF-2α-specific regulatory mechanism, we screened HIF-2α-associated
proteins in a yeast two-hybrid system and identified kelch-like 20 (KLHL20). HIF-2α, but not HIF-1α, interacted with KLHL20. siRNA-mediated knockdown of KLHL20 decreased HIF-2α protein, but not HIF-2α mRNA or HIF-1α protein. Depletion of KLHL20
decreased hypoxia-induced HIF activity, and consequently resulted in
decreased expression levels of HIF-2α-responsive genes such as VEGF and
CITED2. In contrast, overexpression of KLHL20
increased the expression levels and transcriptional activities of the
O(2)-sensitive wild-type and O(2)-insensitive mutant forms of HIF-2α. KLHL20
siRNA also inhibited HIF-2 activity in von Hippel-Lindau tumor
suppressor protein (pVHL)-deficient 786-O cells. These results indicate
that KLHL20 is a novel player that regulates HIF-2α protein expression through mechanisms independent of hypoxia and pVHL.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
EPAS1 , HIF2alpha (2p21)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2034
- Also known as
- HLF; MOP2; ECYT4; HIF2A; PASD2; bHLHe73
- Summary
- This gene encodes a transcription factor involved in the induction of genes regulated by oxygen, which is induced as oxygen levels fall. The encoded protein contains a basic-helix-loop-helix domain protein dimerization domain as well as a domain found in proteins in signal transduction pathways which respond to oxygen levels. Mutations in this gene are associated with erythrocytosis familial type 4. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]
- Expression
- Broad expression in lung (RPKM 304.3), placenta (RPKM 244.1) and 22 other tissues See more
- Extracellular ATP promotes breast cancer invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via hypoxia-inducible factor 2α signaling. Yang H, et al. Cancer Sci, 2019 Aug. PMID 31148343, Free PMC Article
- LncRNA HIF2PUT inhibited osteosarcoma stem cells proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating HIF2 expression. Zhao D, et al. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2019 Dec. PMID 30966832
- LINE-1 and EPAS1 DNA methylation associations with high-altitude exposure. Childebayeva A, et al. Epigenetics, 2019 Jan. PMID 30574831,
- EPAS1/HIF2α correlates with features of low-risk neuroblastoma and with adrenal chromaffin cell differentiation during sympathoadrenal development. Westerlund I, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019 Jan 22. PMID 30563765
- HIF-2α promotes conversion to a stem cell phenotype and induces chemoresistance in breast cancer cells by activating Wnt and Notch pathways. Yan Y, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018 Oct 19. PMID 30340507, Free PMC Article

 Ilias Mylonis
Ilias Mylonis 
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar